What is CBD…and where did it come from?
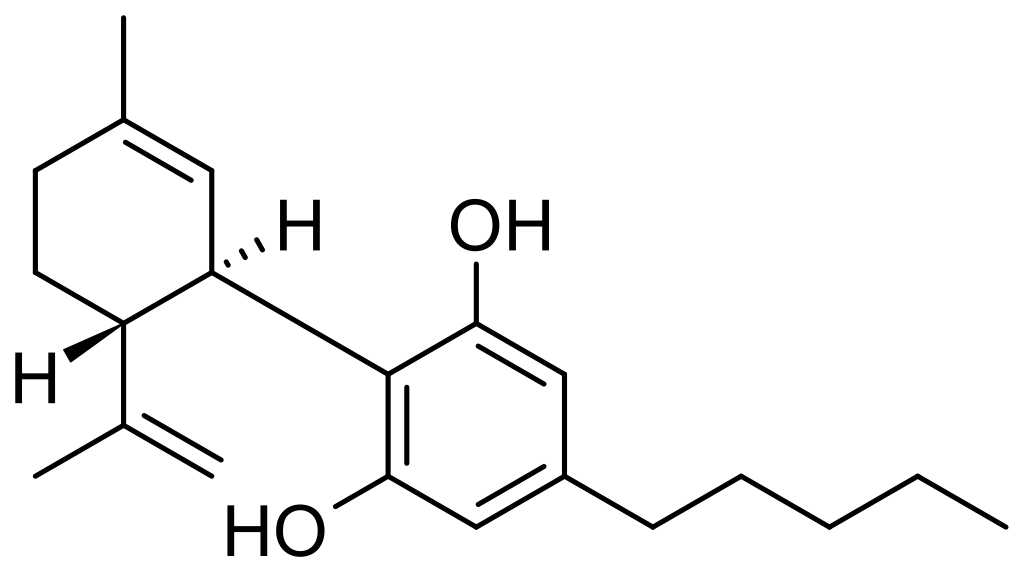
CBD, or cannabidiol, is a phytocannabinoid. Phytocannabinoids (CBD, THC, CBG, etc) are cannabinoids that are produced by the marijuana plant (Cannabis), as opposed to endocannabinoids which are produced in the human body as well as other mammals. Endocannabinoids behave much differently than phytocannabinoids on the cellular level which is why THC and CBD can have such a profound effect on us. Furthermore, humans (and other mammals for that matter) can have an endocannabinoid deficiency, which explains why THC and CBD can have a strong medicinal effect- far more beneficial than just a fleeting recreational high or stubbed toe remedy.
A win-win situation
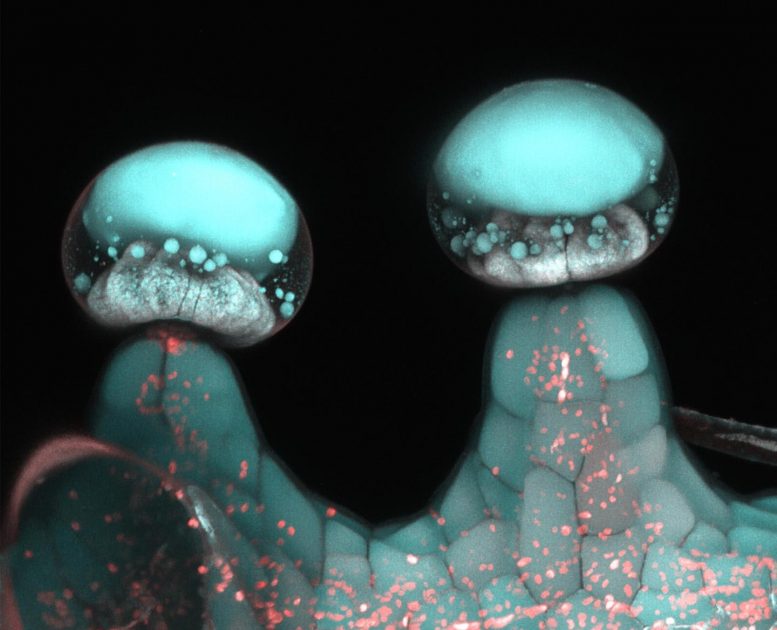
Cannabidiol is produced in tiny glands called trichomes located on the buds of female cannabis plants. Trichomes are microscopic compartments similar to cells, but unlike cells which hold water (cytoplasm), trichomes contain oils such as CBD, THC, and terpenes. Cannabidiol is similar to a plant resin whereas terpenes comprise the essential oil of cannabis. In fact, cannabis has many terpenes in common with other plants such as lavender and pine trees, which is why some cultivars (strains) of cannabis impart a sense of calm or alertness, respectively. The cannabis plant holds many self-preservation interests for producing cannabinoids and terpenes ranging from UV protection, anti-microbial, attracting pollinators, and deterring grazers and pests.
Multi-photon microscopy image of stalked glandular trichome. Credit: Samuels Lab/UBC
Growing on shaky ground
Nearly all cannabis cultivars produce THC and CBD. Because CBD is legal, whereas THC is a Schedule 1 narcotic according to the DEA, much effort is underway to breed out any last trace of THC in hemp. Hemp is defined as the cannabis plant or derivative (extract) having less than 0.3% THC by weight. Although there are currently many hemp cultivars available, a legal problem arises during extraction of the oil from the trichomes to achieve a pure concentrated hemp oil ingredient. The problem is that no extraction method exists which is selective for CBD while leaving behind THC. And because the extraction and purification process effectively concentrates both CBD and THC by a factor of 5 – 20X, what started out as legal hemp with THC levels below 0.3% becomes “drug type” cannabis which is illegal outside of the state-regulated marijuana industries (otherwise known as “hot” extracts). Furthermore, this extract with upwards of 6% THC is very much psychoactive (“high” producing).
The race to breed a hemp cultivar is by necessity, however, not by choice. After all, the hemp oil ingredient usually constitutes such a small percentage of the total weight of a finished consumer product that the mere dilution factor alone during formulation brings the product back in to the legal range of THC (<0.3%) with the exception being a concentrated final product such as a vape cartridge. Thus, the legal risk associated with hot extracts is a transitory one taken on by the manufacturer. It is a risk that most CBD manufacturers are willing to take, as the DEA rarely enforces the law on these “work-in-progress” extracts. This is beneficial to the consumer because CBD and THC have a synergistic or “entourage” effect which can not be achieved by CBD alone. These products are advertised as “full spectrum” because they have higher efficacy but with the drawback of containing trace amounts of THC which could be prohibitive for some consumers.
Find your spot on the spectrum
For those who are intolerant to even the smallest amount of THC due to drug testing, physical sensitivity, or other reasons, there are some chemical purification processes that can remove the THC completely from the extract and, in turn, the final product. If the purification process removes THC but retains other cannabinoids such as CBG or terpenes, the resulting products are advertised as “broad spectrum”. For the minimalist, CBD oil can be purified to its pure form and then formulated to a final product containing no other cannabinoids or cannabis terpenes whatsoever. These final products are labeled neither “broad” nor “full spectrum, but simply as containing “CBD isolate”.
Now that you’re acquainted with CBD and know the difference between Full Spectrum and Broad Spectrum, take a look at some Yesca meds that will brighten your day!